Many DIY tinkerers and small-volume producers are struggling with CNC turning tasks because the material choice in the turning tools, which is called tool steel, is improperly chosen, causing early failure in the parts, a loss in precision, and cost blowouts. The answer to why DIY tinkerers and small-volume producers are struggling with tool steel choice in CNC turning applications begins with the way the trade has traditionally been practiced, with a reliance on traditional know-how rather than scientific data-driven best practices, with a disregard for the important relationship between material properties and machining conditions.
The coming sections will break down the building blocks of a proper material choice in tool steels.
What Key Properties Define Tool Steel Performance for CNC Turning Operations?
Knowledge of the intrinsic properties of tool steel is critical in order to achieve optimal results while performing CNC turning operations. Such properties have a direct impact on the efficiency of the cutting process.
Hardness: Foundation for Wear Resistance
Hardness is the measure of the resistance the material exhibits in undergoing deformation when under load. This is usually tested using the Rockwell C scale. According to the ASM Handbook, as the levels of hardness increase, the wear from the machining processes involving abrasion is reduced. However, the ASM Handbook further states that when the levels of hardness become too high, the resulting material can become less tough. For example, tool steels with a hardness range between 60 and 65 HRC are suitable for high speed machining.
Toughness: Managing the Threat
Toughness refers to the resistance to the absorption of energy prior to fracture, especially under the action of impact or from stress concentrations. In CNC turning, the toughness of the tool can handle intermittent cuts or irregular workloads, such as those occurring in roughing operations. Additionally, materials such as AISI M2 high-speed steel possess high toughness, resulting in minimal chances of tool breakage or chipping. However, toughness can inversely relate to tool hardness.
Thermal Stability & Wear Resistance
Thermostability or hot hardness is the ability of tool steel to maintain its mechanical properties at high temperatures that occur due to high-speed machining. When combined with its wear resistance, it results in reduced edge deterioration due to materials such as stainless steel that have an abrasive nature. The ISO 9001 standard emphasizes the control of the processes to maintain thermal stability in the desired dimensions.
How to Choose Between HSS and Carbide for Different Usages in CNC Turning?
While deciding between high speed steel (HSS) and carbide, some factors need consideration. Both have better performance in different situations.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis of HSS: HSS tools are known for their resilience, which is a great advantage in applications that have complex shapes and require intermittent cutting. The lower cost of ownership resulting from lower set-up costs also favors HSS as it was a limitation to small manufacturers. The disadvantage, however, is that HSS tools may require regular replacements, which is a characteristic that is unfavorable compared to carbide tools.
- Benefits of Carbide in High-Efficiency Machining: The hardness and wear resistance of carbide tools, which are made of a mixture of tungsten carbide particles and a binder of cobalt, make them highly desirable for their speed and extended life when continuous machining is being done. Although the cost of carbide tools is higher initially, their longer life brings down their cost-effectiveness.
- Application-Based Selection Guidelines: In roughing cuts or tough materials, HSS is more desirable because of its ability to withstand impact. On the other hand, carbides are better suited in finishing cuts or machining hard materials such as cast iron. General knowledge available through resources such as the Wikipedia page on “High-speed steel” can be used as a baseline; however, experimentation can confirm the selection.
Why is Heat Treatment Important for the Toughness Properties of Tool Steel?
The heat treatment procedures used affect the structure of the steel used in making the tool steel. The modified structure of the steel makes it possible to have enhanced mechanical properties during the CNC turning operation.
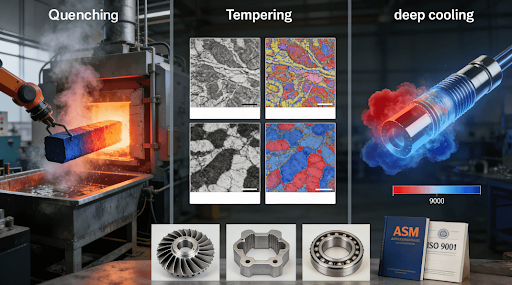
Quenching and Tempering: Microstructural Transformations
Quenching is carried out to cool rapidly to reach high hardness, whereas tempering helps remove brittleness by relieving internal stresses. For instance, tool steels with composition D2 are subjected to oil quenching and tempering at elevated temperatures to attain maximum hardness and toughness. In this way, they are able to enhance wear resistance up to 50% as reported through industry research.
Consistency through Process Standardization
Compliance with the ISO 9001:2015 standard will guarantee the monitoring of the parameters of heat treatment. ISO 9001 certified companies will have strict quality processes in place to maintain consistency from batch to batch. This is more important in case of precise applications, wherein even the slightest deviation may cause the component to be rejected.
Case Study: Heat Treatment in Aerospace Components
In aerospace applications, toolsteels used for CNC turning operations are required to withstand severe conditions. By optimizing the process of heat treatment, tools demonstrate higher resistance against thermal variations, thereby allowing them to work on thermal-resistant alloys. Testing carried out by accredited labs indicates a 30% decrease in tool wear due to optimized heat treatment.
How To Optimize Tool Steel Materials With Difficult Geometric Shapes And Tight Tolerances?
In complex part designs, there is a requirement for higher rigidity and edge stability in the tool steel used in order to maintain accuracy throughout the entire machining process.
- Rigidity and Vibration Damping: The rigidity of the tooling machine plays an important part when evaluating the dimension control of details such as thin-walled sections and deep cavities. The specimen with a high modulus of elasticity will not deform during machining. This complies with ASME Y14.5-2018, which states “The control of geometric tolerance is of major importance in dimension control for fit and function, as a machine tool’s rigidity directly affects the surface finish of the workpieces being machined and the life of the tools.” The lack of vibration means better surface finish and longer tool life.
- Edge Stability for Fine Details: This refers to the ability to maintain its cutting edges under load, a characteristic important for cutting intricate shapes such as micro-threads and edges. The use of high-quality tool steel with fine carbides enhances this process and eliminates the need to keep changing tools from time to time. On how to achieve this, you may need to refer to a CNC turning services guide.
- Balancing Performance with Machinability: Although high-performance tool steels provide many advantages, their machinability is also worth considering in order to prevent excessive tool wear or high processing times. There is simulation software available for predicting the interaction between the tool material and workpieces, providing optimal choices between the demands for machinability.
What Are the Common Mistakes in Tool Steel Selection and How to Avoid Them?
In order to avoid pitfalls when it comes to the selection of tool steel, one has to adopt an organized approach that relies on facts rather than guesses. This is because many pitfalls in the selection of the type of tool steel are the result of not considering certain aspects
Emphasis on Hardness over Toughness
Many users require the greatest hardness possible for fighting the forces of wear, although high hardness will make the material brittle. For example, in intermittent cutting, using a material that is highly hardened may result in chipping. A carefully considered approach will save the user from these material problems.
Ignoring Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Viewing the cost of the tool exclusively, without regard to the long-term cost of replacement, downtime, and scrapped product, misses the mark completely. It is necessary to implement these strategies based on the cost of ownership model, including the length of tool life, speed of machining, and quality rates, to understand the relative economics of the decisions that can be made. Industry benchmarks, as published in Gardner Business Media, state that optimized choices can deliver cost savings of between 20-40%
Overlooking Environment and Operations Issues
Variables such as the type of coolant, machine stability, and operators are connected to tool performance. For example, improper coolant delivery can contribute to thermal fatigue. Risk analysis and proper operational procedures can minimize the impact of such variables.
When Should You Leverage Professional CNC Turning Services for Critical Projects?
In high-stakes environments, professional services ensure expert knowledge is applied, which helps counter risk factors, thereby improving results.
Access to Specialized Material Knowledge
The professional services are also highly informative regarding advanced tool steels, their processing, and other expertise gained from the various sectors. This is highly beneficial when working with exotic materials or with wholly novel designs that exceed current choices.
Certification-Driven Quality Assurance
Aerospace certifications such as AS9100D recognize that the supplier maintains a high standard of quality control processes. These processes eliminate variability in traceability and help to make the component more reliable.
Economic and Efficiency Gains
Outsourcing to qualified service providers might speed up project completion due to more efficient workflow management and usage of advanced technology. For instance, economies of scale in batch production or quick turnaround with high precision in prototyping would be realized.
Conclusion
Choosing an appropriate tool steel for CNC turning services is not only an activity that needs an integrated approach, incorporating material aspects together with economic needs, but it also has much to benefit from adopting an orderly process based on recognized standards. In addition, continued learning will provide further improvement for making informed choices based on changing requirements.
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between HSS and carbide tool steel in the case of CNC turning?
A: High speed steel (HSS) has excellent toughness and shock resistance properties, which are suitable for intermittent cutting. Carbide tools possess high hardness and wear resistance properties, which allow high cutting speed.
Q2: What is the influence of heat treatment on the performance of tool steel?
A: Processes such as quenching and tempering greatly improve the hardness and dimension stability based on changes in the steel’s microstructure. Proper control of these processes can improve the wear resistance by a maximum of 50% depending on the implementation of standards such as ISO 9001.
Q3: Can I use the same tool steel for machining both aluminum and stainless steel?
A: Although doable, the best results are achieved using material-specific selection. Aluminum machining necessitates the use of sharp and polished edges in order to avoid material adhesion, while stainless steel necessitates high hot hardness in an attempt to avoid work hardening issues in machining.
Q4: What are the cost consequences of choosing higher-grade tool steel?
A: Higher grade steel has an initial investment cost that can be 20-40% higher, but can increase tool life by 100% or more. When calculating the cost of ownership, it includes consideration for efficiency and downtime. In this case, it would be an investment worth making for projects that require high-quality output.
Q5: How do certifications such as AS9100D influence the reliability of CNC turning services?
A: The certifications are a guarantee of strict quality management system adherence, with traceability of materials and process validation. They reduce variability in tool steel choice and processing variables. This aspect goes a long way in ensuring risk mitigation with applications involving intense safety requirements, such as aircraft and automobile sectors.

